日本酒造りの主な工程
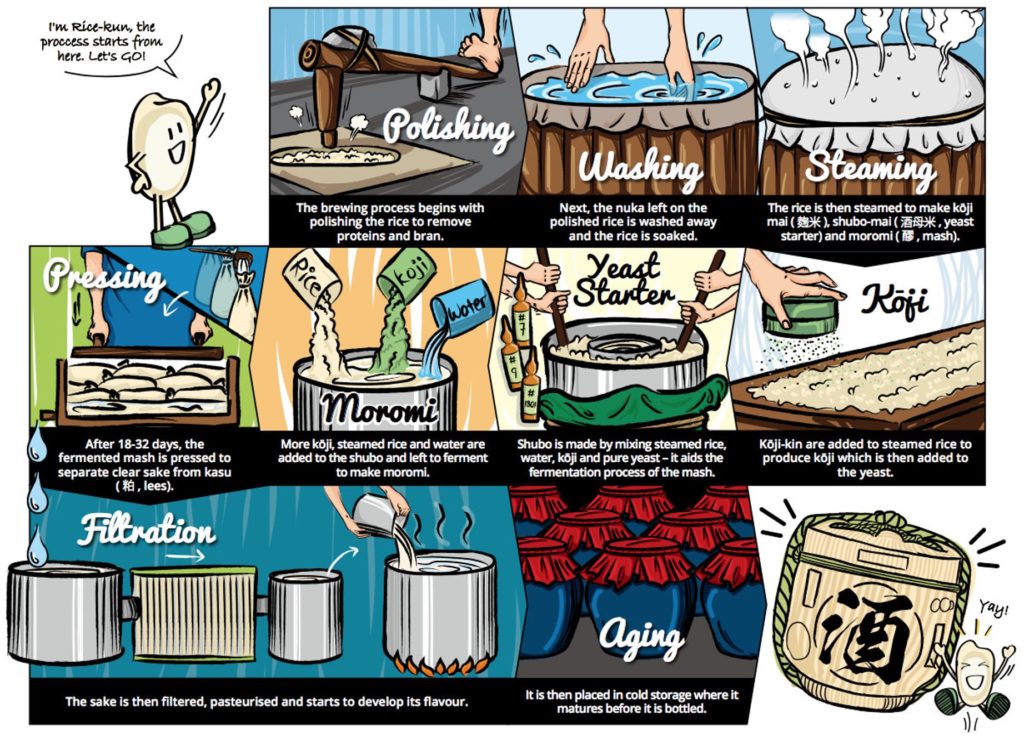
- 精米::米を磨き、酒米を準備します。
- 洗米・浸漬::精米した米を洗い、水に浸けます。
- 蒸米(じょうまい)::米を蒸し、糖化の準備をします。
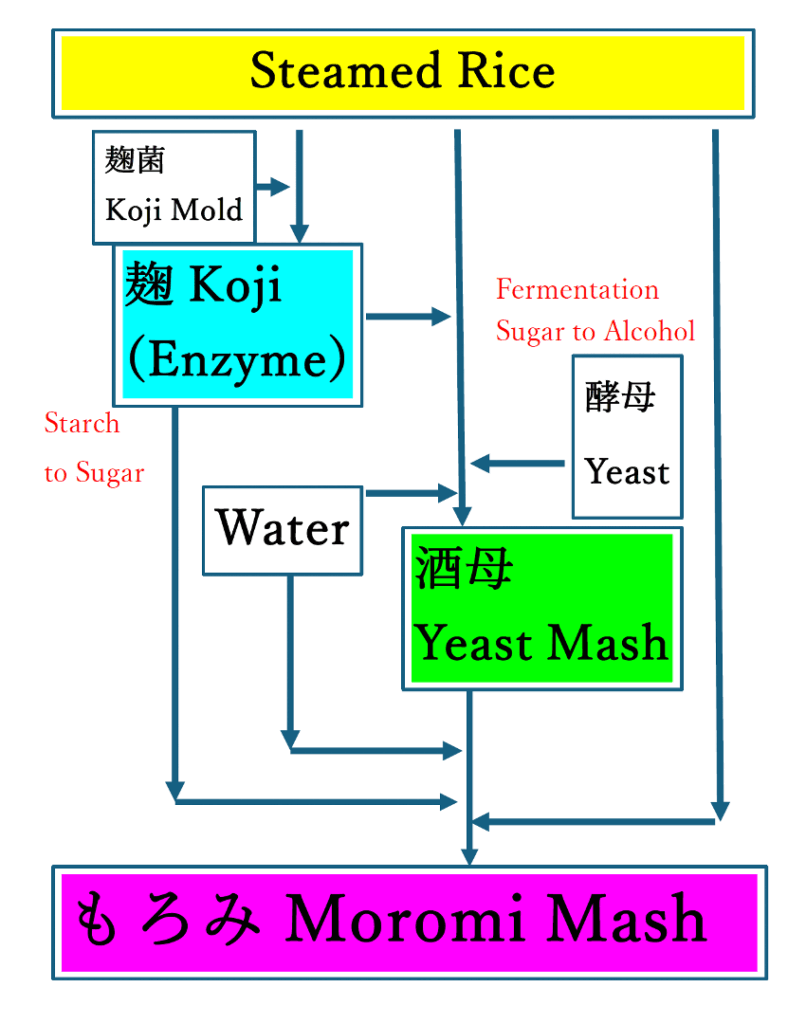
- 製麹(せい麹)::蒸米に麹菌を植え付けて、米のでんぷん質を糖分に変える酵素を作る「麹」を造ります。
- 酒母(しゅぼ)造り::蒸米、麹、水、そしてアルコールを生み出す酵母を加え、酵母を大量に培養します。
- 仕込み(もろみ造り)::酒母に蒸米、麹、水を3段階に分けて加える「三段仕込み」を行います。この「もろみ」が発酵し、アルコールが生成されます。
- 上槽(じょうそう)::発酵したもろみを搾り、日本酒と酒粕に分けます。
- 滓引き・ろ過・火入れ::もろみを搾った後、酒の滓(おり)を沈殿させ、澄んだ部分をろ過します。品質保持のため、熱を加えて殺菌する「火入れ」を行います。
- 熟成・貯蔵::火入れ後、タンクで熟成させ、貯蔵します。
- 瓶詰め::貯蔵したお酒を瓶に詰め、日本酒の完成です。
The Main Steps of Sake Brewing
- Rice Polishing: Polishing the rice to prepare the brewing rice.
- Washing & Soaking: Washing the polished rice and soaking it in water.
- Steaming: Steaming the rice to prepare it for saccharification.
- Koji Making: Inoculating the steamed rice with koji mold to produce enzymes that convert starch into sugar.
- Yeast Starter (Shubo): Combining steamed rice, koji, water, and yeast to cultivate a large amount of yeast.
- Fermentation (Moromi): Adding steamed rice, koji, and water to the yeast starter in three stages (a process called sandan-jikomi). The moromi ferments, producing alcohol.
- Pressing (Jōsō): Pressing the fermented moromi to separate the sake from the sake lees.
- Settling, Filtration & Pasteurization: After pressing, the sediment (lees) is settled, and the clear sake is filtered. It is then pasteurized to ensure quality.
- Aging & Storage: The sake is aged in tanks and stored.
- Bottling: The stored sake is bottled, completing the process.